Main menu:
Bolivien
Introduction |
||
Flag: |
||
Card: |
||
Background: |
Bolivia, named after independence fighter Simon BOLIVAR, broke away from Spanish rule in 1825; much of its subsequent history has consisted of a series of nearly 200 coups and counter-coups. Comparatively democratic civilian rule was established in the 1980s, but leaders have faced difficult problems of deep-seated poverty, social unrest, and drug production. Current goals include attracting foreign investment, strengthening the educational system, continuing the privatization program, and waging an anti-corruption campaign. |
|
Geography |
||
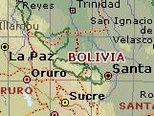
Location: |
Central South America, southwest of Brazil |
|
Geographic coordinates: |
17 00 S, 65 00 W |
|
Map references: |
South America |
|
Area: |
total: 1,098,580 sq km |
|
Coastline: |
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims: |
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate: |
varies with altitude; humid and tropical to cold and semiarid |
|
Terrain: |
rugged Andes Mountains with a highland plateau (Altiplano), hills, lowland plains of the Amazon Basin |
|
Elevation extremes: |
lowest point: Rio Paraguay 90 m |
|
Geography - note: |
landlocked; shares control of Lago Titicaca, world's highest navigable lake (elevation 3,805 m), with Peru |
|
People |
||
Population: |
8,300,463 (July 2001 est.) |
|
Nationality: |
noun: Bolivian(s) |
|
Ethnic groups: |
Quechua 30%, Aymara 25%, mestizo (mixed white and Amerindian ancestry) 30%, white 15% |
|
Religions: |
Roman Catholic 95%, Protestant (Evangelical Methodist) |
|
Languages: |
Spanish (official), Quechua (official), Aymara (official) |
|
Gouvernment |
||
Country name: |
conventional long form: Republic of Bolivia |
|
Government type: |
republic |
|
Capital: |
La Paz (seat of government); Sucre (legal capital and seat of judiciary) |
|
Flag description: |
three equal horizontal bands of red (top), yellow, and green with the coat of arms centered on the yellow band; similar to the flag of Ghana, which has a large black five-pointed star centered in the yellow band |
|
Economy |
||
Economy - overview: |
Bolivia, long one of the poorest and least developed Latin American countries, has made considerable progress toward the development of a market-oriented economy. Successes under President SANCHEZ DE LOZADA (1993-97) included the signing of a free trade agreement with Mexico and joining the Southern Cone Common Market (Mercosur), as well as the privatization of the state airline, telephone company, railroad, electric power company, and oil company. His successor, Hugo BANZER Suarez has tried to further improve the country's investment climate with an anticorruption campaign. Growth slowed in 1999, in part due to tight government budget policies, which limited needed appropriations for anti-poverty programs, and the fallout from the Asian financial crisis. In 2000, major civil disturbances in April, and again in September and October, held down overall growth to 2.5%. |
|
Industries: |
mining, smelting, petroleum, food and beverages, tobacco, handicrafts, clothing |
|
Agriculture - products: |
soybeans, coffee, coca, cotton, corn, sugarcane, rice, potatoes; timber |
|
Exports: |
$1.26 billion (f.o.b., 2000 est.) |
|
Currency: |
boliviano (BOB) |
|
Currency code: |
BOB |
|
Transportation |
||
Railways: |
total: 3,691 km (single track) |
|
Highways: |
paved: 2,500 km (including 30 km of expressways) |
|
Waterways: |
10,000 km (commercially navigable) |
|
Ports and harbors: |
none; however, Bolivia has free port privileges in maritime ports in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, and Paraguay |
|
Coffee |
||
Bolivia is a conundrum ... a perfect coffee-producing locale in terms of altitude, soil types, weather. But Bolivia has traditionally had trouble producing consistently high quality coffee. I thought it was an origin we would never stock but a recent arrival sample has proved me wrong, a cup with a sweet cinnamon spiciness, a cup whose charm emerges as it cools. The best growing areas are in the western mountains, adjacent to the Peruvian border and near the Cuzco region. Much of the coffee is grown cooperatively by very small farms (many less than 3 hectares |
||
|
|
|
The predominantly grown Arabica from the 1,200m high altitude Ngozi is characterized by substantial acidity and a very full flavor. |
||